The Internal Revenue Service has announced the 2024 cost-of-living adjustments (COLAs) for benefit plans. They are as follows:
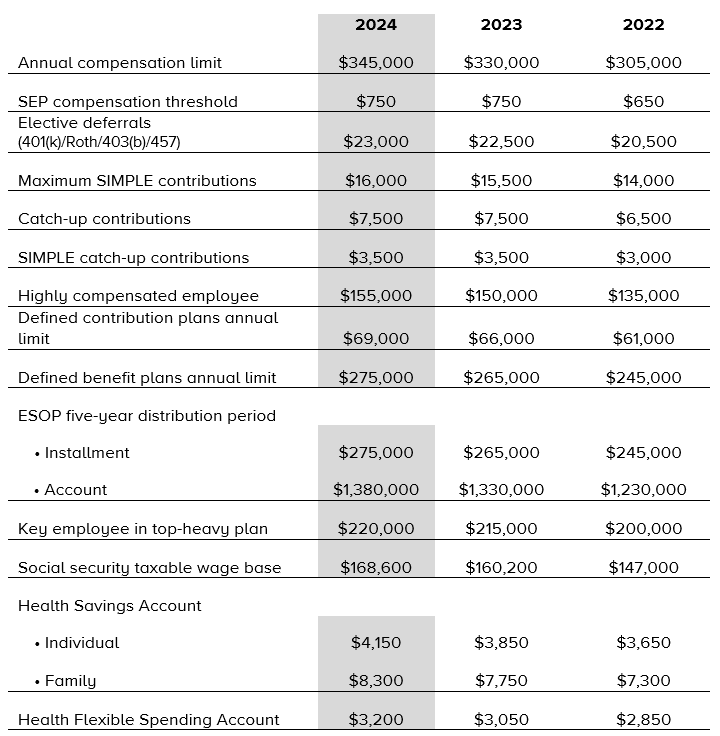
- Annual compensation limit. The compensation limit (IRC 401(a)(17)) applies for calculating benefits and contributions, for general and 401(k) discrimination testing and for determining tax deductions.
- Elective deferrals (401(k)/Roth/403(b)/457). The calendar year contribution limit applies to pre-tax and Roth salary deferrals.
- Catch-up contributions. The calendar year dollar limitation applies for catch-up elective deferral contributions for individuals who, in 2024, are age 50 or above.
- Highly compensated employee. A “highly compensated employee” is one who (a) was a more-than-5 percent owner during the year or the preceding year, or (b) for the preceding year (i) had compensation in excess of $155,000 and (ii) if the employer elects for the plan year, was in the top-paid group (top 20% of pay) of employees.
- Defined contribution plans annual limit. The annual dollar limitation on total additions (both deferrals and employer contributions) applies to defined contribution plans for plan limitation years ending in 2024.
- Defined benefit plans annual limit. For plan limitation years ending in 2024, the annual dollar benefit limitation under a defined benefit plan has increased to $275,000. For participants who separated from service before January 1, 2024, the 100 percent of average high-three-years’ compensation limit is computed by multiplying the participant’s compensation limitation, as adjusted through 2023, by 1.0351.
- ESOP five-year distribution period. The dollar amount used in determining the maximum account balance in an employee stock ownership plan subject to a five-year distribution period has increased to $1,380,000 in 2024, while the dollar amount used to determine the lengthening of the five-year distribution period is increased to $275,000.
- Key employee in top-heavy plan. In defining who is a key employee in a top-heavy plan, for plan years ending in 2024, the compensation threshold for an officer has increased to $220,000.
- Social security taxable wage base. The social security taxable wage base is the limit over which the retirement portion of FICA/FUTA taxes is not assessed (however, Medicare taxes are still collected).




